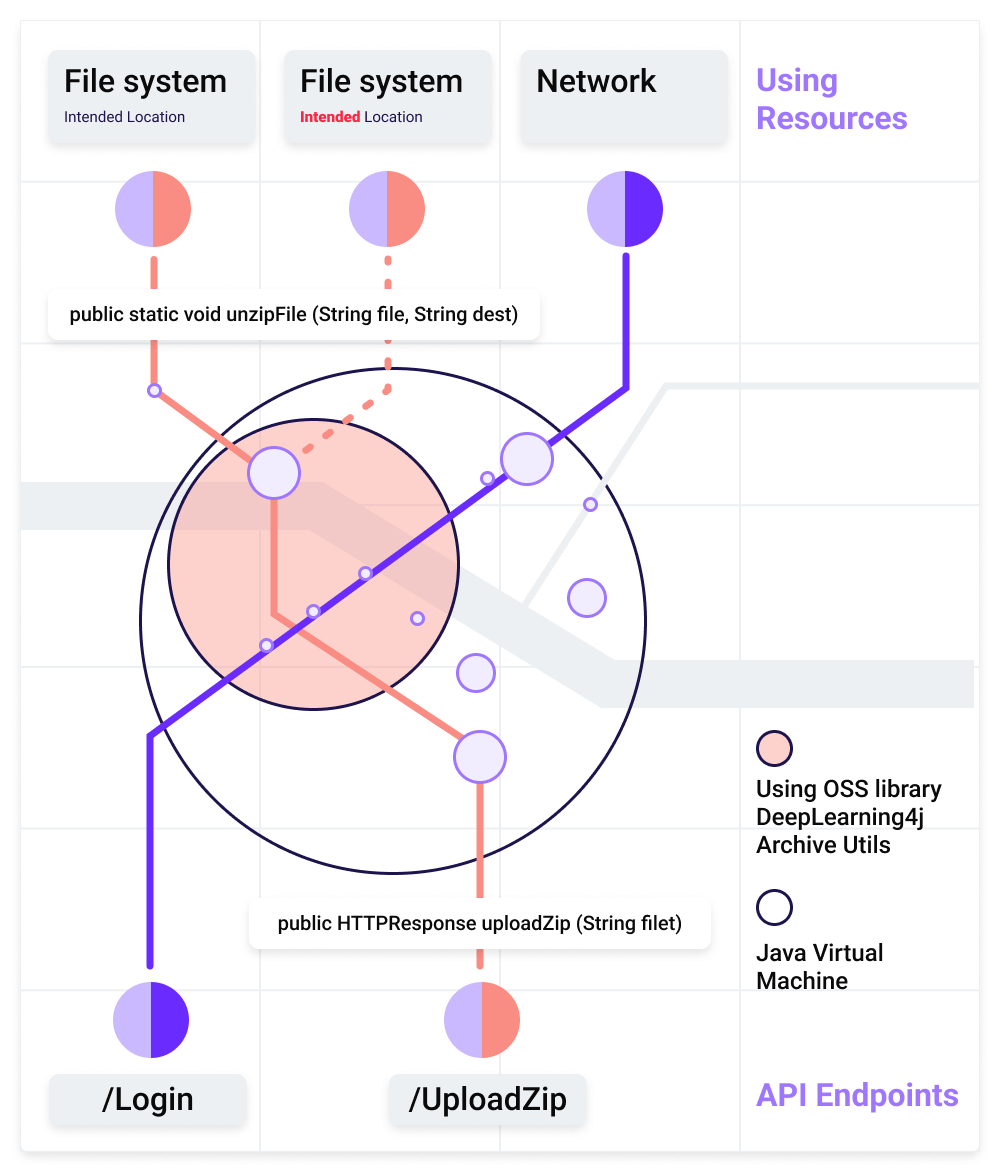
Digital transformation drives everything in our daily lives.
Adoption of mobile is at the heart of this paradigm shift. For instance, mobile apps contributed to a staggering 230 billion total downloads in 2021, with over $170 billion spent on the app store. This trend only appears to grow and will reach 7.49 billion mobile users by 2025.
The increased use of digital platforms and applications calls for more robust technologies to ease the development and deployment of application bundles. It’s common for application developers to use some form of zip archive considering the wide range of use cases.
Zip archives are capable of many versatile applications, such as combining multiple files into a single file for ease of transport. A single zip file allows the users to upload the required data efficiently, and the backend can extract the archive to obtain the individual files.
What is a Zip file?
A zip file is a method that uses file compression to bundle multiple files into a single file making it easier for users to transfer files across the internet. A zip archive’s primary benefit is the ability to compress large files to consume less storage space and bandwidth.
React ecosystem modules distribution of vulnerability types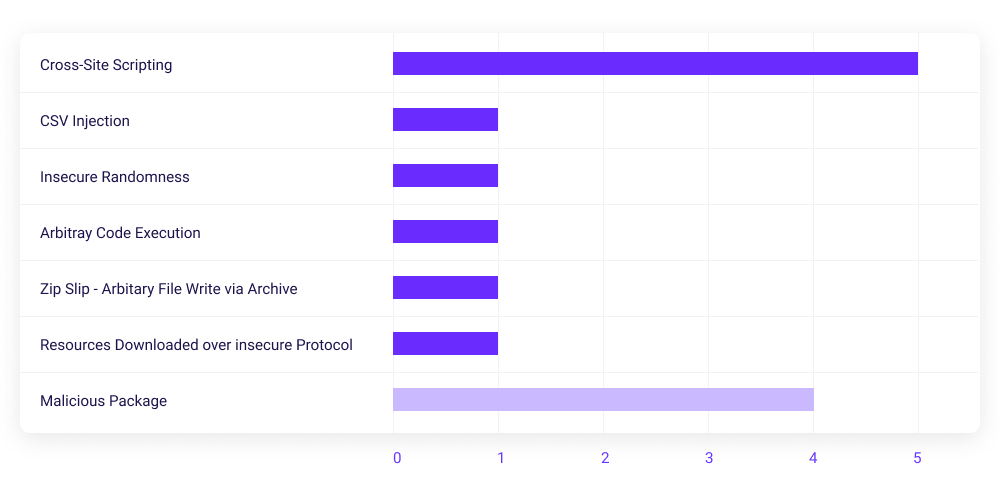
With the broad introduction of archiving and compression technologies, zip takes dominance due to its widespread use and compatibility across multiple computing systems.
However, with its universal adoption, the zip archive becomes a target for malicious attackers to cause damage to computer systems.
What is a Zip Slip vulnerability attack?
Disclosed in June 2018 by Snyk, the zip slip vulnerability causes arbitrary file overwrite operations that may lead to remote code execution.
According to the disclosure, the vulnerability appears in standalone functions and within the applications that use these vulnerable libraries to process archives. In addition, it affects multiple arrays of archive formats, including jar, tar, cpio, war, apk, 7z, and rar, and is also prevalent within multiple ecosystems that use Ruby, JavaScript, .Net, and Java.
The tactic behind the zip slip vulnerability is simple yet deadly. This vulnerability exploits the system’s capability to extract archives and uses this to overwrite predefined files. It can then lead to remote code execution depending on the payload stored within the archive.
The following files below display the payloads capable of exploiting the zip slip vulnerability present within a remote system:
When extracting these files, the system may extract the “good.sh” file into the expected directory. However, the file containing multiple “../” escape characters within its file name would cause similar behavior to directory traversal and reach the system’s root directory. Therefore, instead of extracting the file into the expected directory, the file would otherwise extract itself into the “/tmp” directory causing an arbitrary file overwrite.
This file can contain any payload. An attacker may configure the payload to perform remote code execution by overwriting a file that would require a user to execute or an automatic execution by the system itself.
What are the risks of a Zip Slip attack to your organization?
The zip slip attack poses many risks to an organization; these risks can directly impact the customers, users, and applications used within the organization. In addition, some cybersecurity attacks can have dire financial consequences, meaning that the most overlooked aspect is the reputational damage to a brand’s image.
The direct impact of this type of attack may depend on the sensitivity of the affected system. Therefore, some of the considerable risks of this attack include:
- Arbitrary file overwrite – The attacker overwrites a file within the system with a custom file.
- Code execution – The attacker executes commands on the victim’s system to perform a predefined set of actions, which are often malicious.
- Overwriting sensitive resources – The attacker successfully overwrites sensitive files or information within a system; this can lead to the destruction of valuable information.
- Remote Command Execution on victim’s machine – The attacker executes remote commands of a machine that they do not have physical access to, which would compromise the victim’s machine.
Who is vulnerable to a Zip Slip attack?
Organizations that use systems and applications with affected libraries are vulnerable to the zip slip attack. Upon further analysis, researchers identified that the most affected language is Java due to the lack of a central library to process archives. However, other languages are also vulnerable.
Synk’s GitHub repository contains a comprehensive list of vulnerable and affected libraries. At the time of writing this article, almost all of the affected libraries contain fixes.
A common misconception that organizations have is searching for the affected library directly within their installed list of software or applications. However, this will not reveal the affected libraries as the applications may directly or indirectly use these affected libraries.
The most effective method is to go through the list of libraries used by a single application and check if it contains any of the affected libraries.
Step by step guide to protecting against Zip Slip attacks
Understanding the impact and the vast range of applications affected by this vulnerability is crucial. Some of the most significant affected projects include Oracle, Amazon, Spring/Pivotal, Linkedin, Twitter, Alibaba, Jenkinsci, Eclipse, OWASP, SonarQube, OpenTable, Arduino, ElasticSearch, Selenium, JetBrains, and Google.
There are various methods that an organization may employ to protect themselves against the zip slip attack. Some of the basic principles to follow are:
- Search Snyk’s list of impacted libraries – is yours on there?
- Add zip slip testing to your build pipeline
- Invest in your DevSecOps
Search Snyk’s list of impacted libraries – are libraries you use on the list?
The most straightforward method is to search through Synk’s list of impacted libraries and ensure that it does not contain any of the libraries used within the organization.
However, it is not as easy to obtain a comprehensive list of all the libraries that every application uses. In these instances, the software vendor or developer may help identify the library or directly identify whether the zip slip vulnerability affects the current version of the software.
Add Zip Slip testing to your build pipeline
If there are in-house application development teams, they will need to check within all the existing code to ensure they are not running a vulnerable library version.
Doing this manually is a very time-consuming task. Therefore the best alternative is to introduce automation. OX Security automatically blocks vulnerabilities introduced into your pipeline and ensures the integrity of every workload.
Invest in your DevSecOps
DevSecOps is a proven framework that allows existing DevOps teams to incorporate security within their development lifecycle. A traditional DevOps lifecycle focuses its efforts on continuous deployment that allows developers to keep submitting new releases more regularly.
However, these regular releases render the traditional security testing mechanisms ineffective, aiming to test an entire application after a successful build process. Instead, a successful DevSecOps implementation enables developers to continually monitor software supply chain security to avoid and patch vulnerabilities before they reach production. This can be in the form of secure coding and ensuring that none of the libraries contain vulnerabilities.
DevSecOps revolutionizes the development process by allowing teams to build secure applications much faster than they ever could with traditional models.
Visibility and automation play vital roles. Technologies such as OX Security allow modern DevOps teams to integrate their existing CI/CD pipelines while introducing new capabilities that help protect against supply chain risks, other build-stage vulnerabilities and more.
Stay secure to protect against cyber attacks
The zip slip vulnerability perfectly demonstrates that new vulnerabilities will always appear, no matter what controls the developers build into the code. Detecting and patching these vulnerabilities can take a lot of time from the build stages. OX Security drives unparalleled versatility and cuts down on the time required to detect and remediate these vulnerabilities.
Book a demo or try for free today to put your code through its paces and identify vulnerabilities lurking beneath the surface.